FORM FOLLOWS FUNCTION
What does ‘Form follows Function’ veritably mean? The quote purely states that the purpose of the structure or space defines the appearance of it. This principle presides over and lays down a foundation in any project of any form. It is important to understand
- what exactly do ‘form’ and ‘function’ individually mean,
- how are they correspondent and
- who coined the theory
Form
Form in architecture is the liaison between space and mass. Form is definitely a significant part of architecture, yet it is also a supremely debated topic. The form incorporates many elements apart from just a shape or arrangement of the structures. It considers multiple aspects like size, materials, manufacturing, and process. There are categories of forms like:
- regular forms
- irregular forms
- mixed forms
- inspired by nature
- unusual forms
- forms in the interior
- geometrical and architectural forms, etc.
The expertise of the designer determines the caliber of the architecture via how the architect can use and correlate the above elements, both in the open spaces that surround the building as well as interior spaces.
Function
The function is primarily the use of the space or structure. Buildings often have a broad- spectrum of functions like, a house that has a single function or an office building that can have a combination of functions like office, restaurant, retail shops, etc. Though functionalism is a principle under which buildings are designed solely based on the purpose of the structure, yet in reference to modern architecture this principle creates confusion and is debatable. Having said that the user should be satisfied with the functional needs, it is fairly important to consider the shape of the structure too.
Form follows Function
Louis Sullivan coined the phrase ‘Form ever follows function’; he is known as the father of skyscrapers and modernism. By saying so, he meant that the purpose interprets how space or structure will look and determine its efficiency. He showcased an exquisite balance between art and modernism through the form. This ideology implies that architectural ornaments (decorative elements) are unproductive in modern architecture, though it does not imply that all decorative elements are useless. Moreover, this concept does not mean that the function eliminates the form, but it conveys that the form of a building is an articulation of its function.
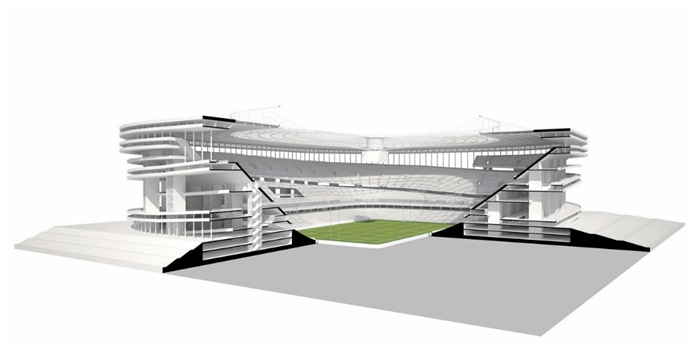
Furthermore, taking the example of a stadium, the main function of it is to let the audience watch an event. The structure thus got the form with an open area in the center which is surrounded by seating spaces for the viewers in a step fashion. All the stadiums follow the same form with additional features though the chief forms remain persistent. Similarly, while designing a house it is essential to study the lifestyle and daily routine of the client. Depending on this study it will be easy to place the spaces and thus attain the find form which will be the outcome of the functional analysis.
Frank Lloyd Wright was Sullivan’s subordinate, he took over Sullivan’s thought and endorsed it further. He applied this principle in his project ‘The Guggenheim Museum’. The form has the integration of a spiral shape that is consciously designed to assist visitors in viewing the artwork in the museum.

Inference
To conclude, designing is nothing but ‘decision’ making. The form is the appearance of the structure or space and function is the purpose of it. Louis Sullivan said ‘form ever follows function’ which suggests that form can be concluded after analyzing and understanding the function of the space or structure to be designed. Moreover, he meant that function does not dominate form but assists in designing one logically.
References:
- https://mfareview.wordpress.com/2011/10/21/function-follows-form-rethinking-the-%E2%80%98function%E2%80%99-of-%E2%80%98form%E2%80%99-in-architecture/
- https://www.slideshare.net/sajidashah14/form-follows-function-52819245
- https://www.thoughtco.com/form-follows-function-177237
- https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2010/03/does-form-follow-function/
- https://www.slideshare.net/pathyapustak/form-follows-function-15146540
- https://www.planndesign.com/articles/2758-importance-form-architecture
